The method of presenting the results of clinical studies can affect their interpretation by clinicians2 and nonclinicians alike3,4 Therefore, it is important to understand the different ways in which results can be presented Absolute risk refers to the simple event rate in a group of people who receive an intervention (see Example 1)Can hazard ratios and odds ratio be used interchangeably in metaanalysis?The odds ratio (OR) is the ratio of odds of an event in one group versus the odds of the event in the other group An RR (or OR) of 10 indicates that there is no difference in risk (or odds) between the groups being compared An RR (or OR) more than 10 indicates an increase in risk (or odds) among the exposed compared to the unexposed, whereas a RR (or OR)
2
Odds ratio vs hazard ratio interpretation
Odds ratio vs hazard ratio interpretation- Odds ratio 1 ODDS Chance of event occurring divided by chance of event not occurring › For example, in 100 births, the probability of a delivery being a boy is 51% and being a girl is 49% › The odds of a delivery being a boy is 51/49 = 104 In simpler term, an odds of an event can be calculated as Number of events divided by number of noneventsThe hazard ratio interpretation is a little clunky It tells you the risk of an event in the intervention group compared with the control group at any particular point in time For example, a hazard ratio of 05 tells you that, at any particular point in time, the




Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1
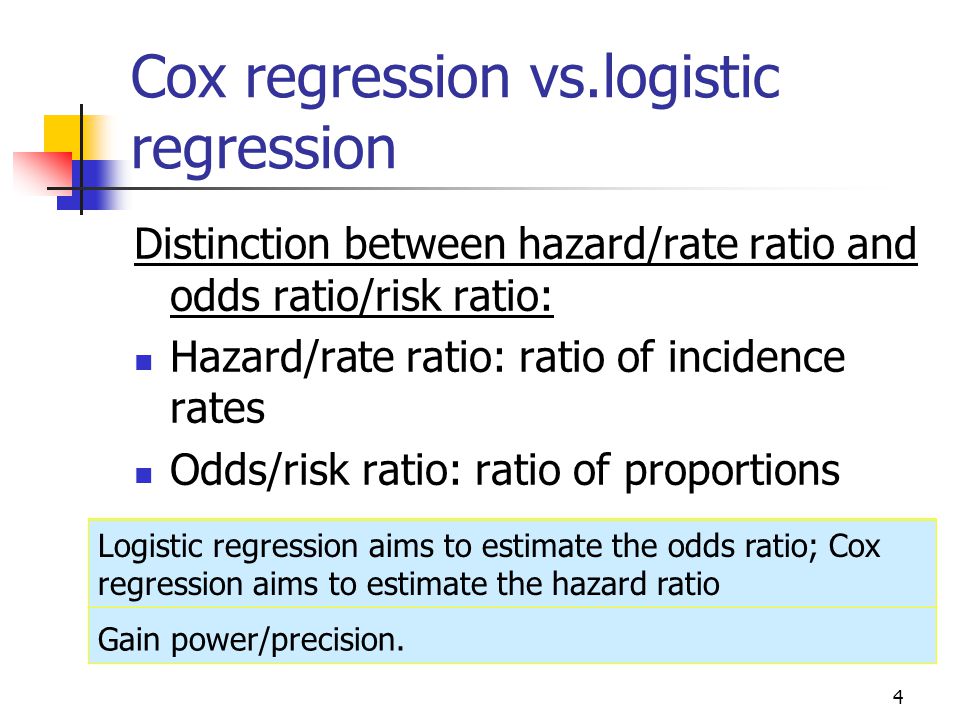
Ratio and odds ratio/risk ratio – Hazard/rate ratio ratio of incidence rates – Odds/risk ratio ratio of proportions By taking into account time, you are taking into account more information than just binary yes/no Gain power/precision Logistic regression aims to estimate the odds ratio;Odds Ratio Odds Ratio for comparing two proportions OR > 1 increased risk of group 1 compared to 2 OR =√100以上 hazard ratio vs odds ratio Hazard ratio vs odds ratio interpretation The method of presenting the results of clinical studies can The hazard ratio would be 2, indicating higher hazard of death from the treatment Hazard ratios differ from relative risks (RRs) and odds ratios (ORs) in that RRs and ORs are cumulative over an entire study, using a defined endpoint, Hazard Ratio (ie the ratio of hazards) = Hazard in the intervention group ÷ Hazard in the control group Hazard represents the instantaneous event rate, which means the probability that an individual would experience an event (eg death/relapse) at a particular given point in time after the intervention, assuming that this individual has survived to that particular point of time
P less than 0001);Hazard ratio vs odds ratio interpretation Are odds ratio and hazard ratio the same Odds = P (positive) / 1 – P (positive) = (42/90) / 1 (42/90) = (42/90) / (48/90) = 0875 Thus, the odds ratio for experiencing a positive outcome under the new treatment compared to the existing treatment can be calculated as Odds Ratio = 125 / 0875 = 1428 We would interpret this to meanThis video wil help students and clinicians understand how to interpret hazard ratios
The risk ratio (or relative risk) is the ratio of the risk of an event in the two groups, whereas the odds ratio is the ratio of the odds of an event (see Box 92a ) For both measures a value of 1 indicates that the estimated effects are the same for both interventionsUn odds ratio de 2,07 qui implique une 01 augmentation (ou la diminution) de l' Thoughts affecter les chances de prendre (ou ne pas prendre) Si vous avez mis prédicteurs, alors l'interprétation est la même, sauf le "changement d'une unité" signifie 1 écarttype Si vous souhaitez que les valeurs de mise à l'échelle et non mis à l'échelle de prédicteurs, il est probablement plusThis corresponds to a MantelHaenszel–adjusted odds ratio of 50 for Table 4 and 279 for Table 5 However, all of these odds ratios lack any interpretation as an average



Hazard Ratios And Survival Curves Youtube



Odds Ratio Hazard Ratio And Relative Risk Janez Stare Semantic Scholar
Cox regression aims to estimate the hazard ratio 10 Risks vs Rates Relationship between risk andRisque avec la préparation X ?If not how can I convert hazard ratio to odds ratio?




Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios




Hazard Ratio Measure Of Survival Or Time To Event Analysis Same As Relative Risk 1 Means The Hazard Ratio Analysis University Of Alabama At Birmingham
Risk ratios, odds ratios, and hazard ratios are three common, but often misused, statistical measures in clinical research In this paper, the authors dissect what each of these terms define, and provide examples from the medical literature to illustrate each of these statistical measures Finally, the correct and incorrect methods to use these measures are summarized Keywords Risk ratios, odds ratios, and hazard ratios are three ubiquitous statistical measures in clinical research, yet are often misused or misunderstood in their interpretation of a study's results 1 A 01 paper looking at the use of odds ratios in obstetrics and gynecology research reported 26% of studies (N = 151) misinterpreted odds ratios as risk Hazard Ratio (HR) and relative risk (RR) are widely used effect size index in clinical research According to the calculations from Chen et al (10), OR = 168, 347, and 671 are equivalent to Cohen's d = 02 (small), 05 (medium), and 08 (large), respectively, when disease rate is 1% in the nonexposed group In this paper, we calculated Cohen's d for a given HR and RR



Hazard Ratio Vs Odds Ratio ただの悪魔の画像




Main Results Of The Comparison Between The Hazard Ratio Hr Odds Download Table
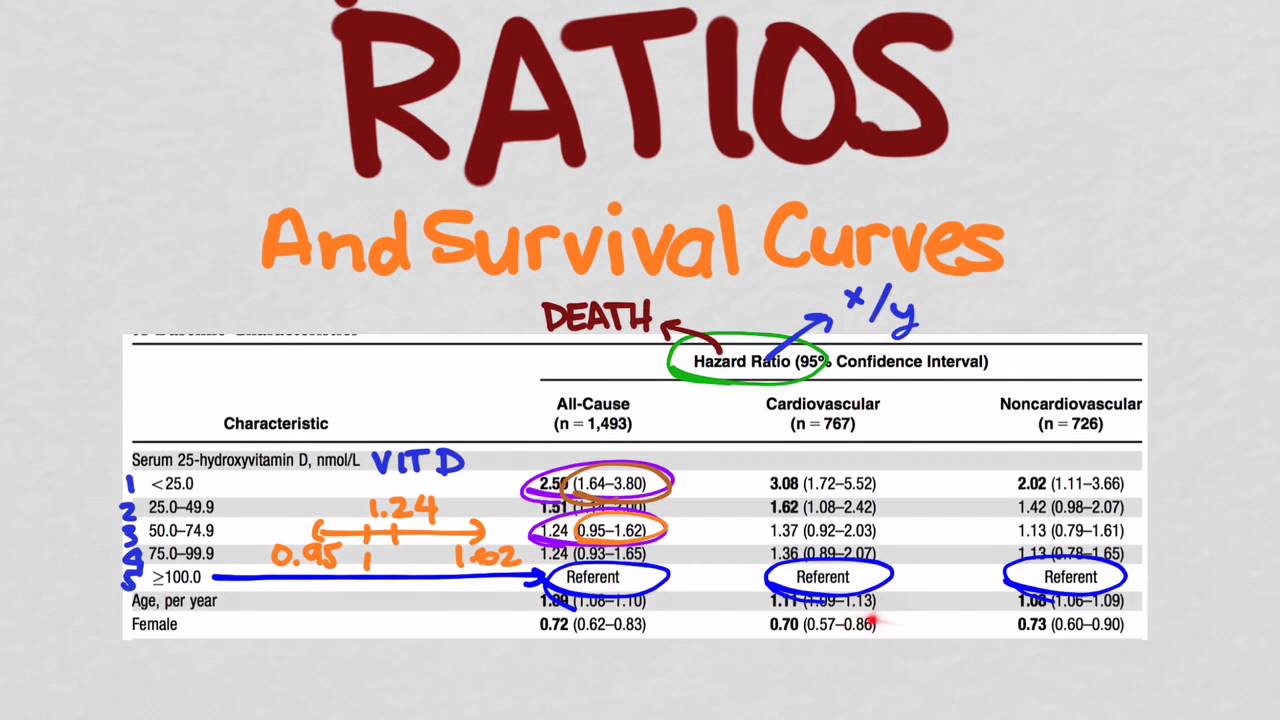
Hazard ratio (E vs C) for the time period Please note that results shown are rounded to 2 decimal places, but the calculations used the The interpretation of a hazard ratio is essentially the same as an odds ratio However it's probably worth noting that whilst an odds ratio is derived from calculating the odds of an event in the intervention and the control arms expressed as a ratioL'OR est proche du RR lorsque le nombre d'événements est faible Cependant, dans une étude castémoins, seul l'odds ratio peut être estimé puisque le nombre total de sujets non malades est déterminé par le nombre de témoins choisis par cas Le Hazard Ratio (HR) est proche du RR avec une dimension temporelle supplémentaire En effet, dès lors que l'on est en présence de données



Relative Risk Ratios And Odds Ratios



Use And Interpret Chi Square In Spss
Hazard ratio for progression or death, 034; Odds Ratio • How many times more likely the odds of finding an exposure in someone with disease is compared to finding the exposure in someone without the disease • Interpretation – OR > 1 Increased frequency of exposure among cases – OR = 1 No change in frequency of exposure – OR < 1 Decreased frequency of exposure 9Logistic regression log (odds) = The hazard ratio of death for surgery vs no surgery is assumed to be the same at any time since baseline The model may therefore be called "a constant hazard ratio model", but someone thought that "proportional" is a better word to describe a fixed ratio of two hazards over time (When the ratio of two quantities is fixed, we may say that one




Crude And Adjusted Measures Of Odds Ratio Or And Hazard Ratio Hr Download Table




A Beginner S Guide To Interpreting Odds Ratios Confidence Intervals And P Values Students 4 Best Evidence
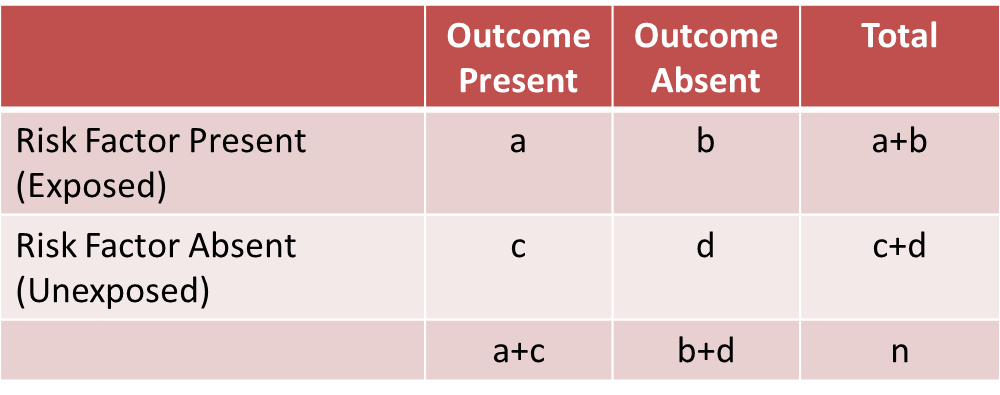
Interpretation of the Hazard Ratio Hazard ratios of interest are derived using the regression coefficient of the Cox model and can reflect comparison of two different sets of covariate values as shown previously or a single covariate If, for example, the covariate X i is status for a particular risk factor (0 for risk factor absent, 1 for risk factor present), then the hazard ratio is Hazard ratio (E vs C) for the time period Please note that results shown are rounded to 2 decimal places, but the calculations used the raw numbers from the previous column ( c ) and therefore give different results than if the rounded numbers were used (eg, 006/008 = 075)A significant benefit was also observed with respect to the confirmed objective response rate and the time to




Logistic Regression And Survival Analysis



Hazard Ratio
An odds ratio of 2 means that the event is 2 time more probable given a oneunit increase in the predictor It means the odds would double, which is not the same as the probability doubling In Cox regression, a hazard ratio of 2 means the event will occur twice as often at each time point given a oneunit increase in the predictorRather the odds is threefold greater Interpretation of an OR must be in terms of odds, not probability Again, the OR will95% confidence interval, 025 to 047;




Relative Risk And Odds Ratio




The Difference Between Relative Risk And Odds Ratios The Analysis Factor
ベスト hazard ratio vs odds ratio interpretation 69Are odds ratio and hazard ratio the same HR > 1 increase in the hazard; The hazard ratio, sometimes called a relative hazard, is typically used to compare time to event data between two treatment groups The hazard ratio of death for the intervention group compared with the control group was 046 (022 to 095) The hazard ratio was derived as the ratio of the hazard of death for the intervention group to the hazard of death for theRelative risks, odds ratios and hazard ratios?



Hazard Ratio Calculator Calculate Hazard Ratio Hr Confidence Intervals P Value



1
Risk ratios, odds ratios, and hazard ratios are three ubiquitous statistical measures in clinical research, yet are often misused or misunderstood in their interpretation of a study's results 1 A 01 paper looking at the use of odds ratios in obstetrics and gynecology research reported 26% of studies (N = 151) misinterpreted The basic difference is that the odds ratio is a ratio of two odds (yep, it's that obvious) whereas the relative risk is a ratio of two probabilities (The relative risk is also called the risk ratio) Let's look at an example Relative Risk/Risk Ratio Suppose you have a school that wants to test out a new tutoring program At the start of the school year they impose the new tutoringMore on the Odds Ratio Ranges from 0 to infinity Tends to be skewed (ie not symmetric) "protective" odds ratios range from 0 to 1 "increased risk" odds ratios range from 1 to Example "Women are at 144 times the risk/chance of men" "Men are




A Meta Analysis Of Adjusted Hazard Ratios From Observational Studies Of Bilateral Versus Single Internal Thoracic Artery Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting The Journal Of Thoracic And Cardiovascular Surgery




How To Be Awesome At Biostatistics And Literature Evaluation Part Ii Tl Dr Pharmacy
Risk Ratio vs Odds Ratio Whereas RR can be interpreted in a straightforward way, OR can not A RR of 3 means the risk of an outcome is increased threefold A RR of 05 means the risk is cut in half But an OR of 3 doesn't mean the risk is threefold; Risk ratios, odds ratios, and hazard ratios are three ubiquitous statistical measures in clinical research, yet are often misused or misunderstood in their In cohort A, imagingbased progressionfree survival was significantly longer in the olaparib group than in the control group (median, 74 months vs 36 months;



Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1




1 Relative Risks Odds Ratios Or Hazard Ratios Of Risk Factors For Download Table
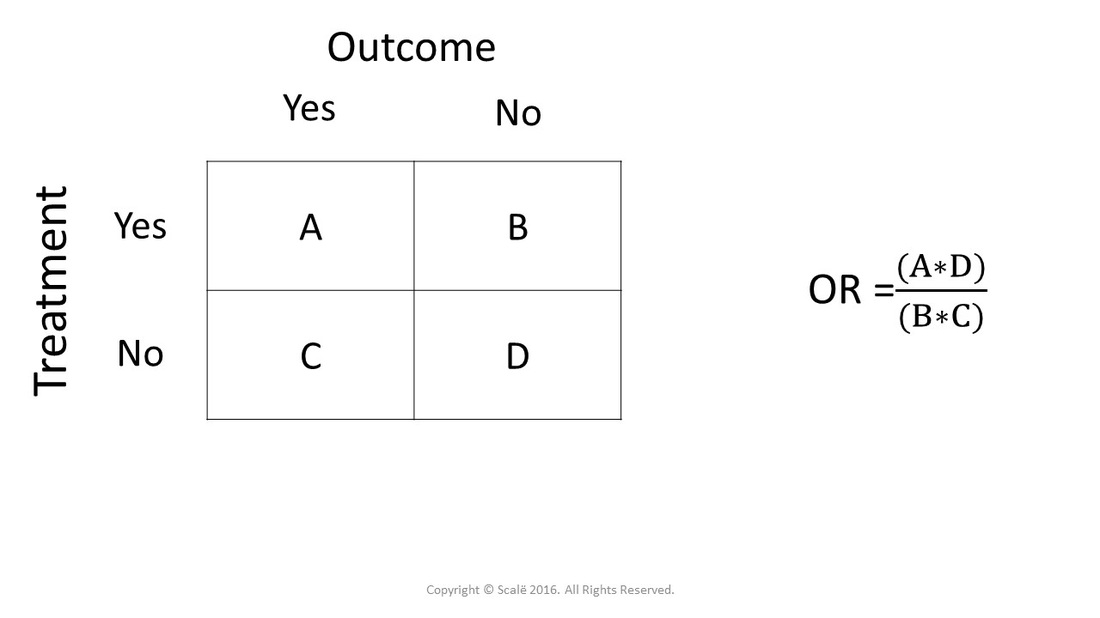
The odds ratio is calculated as Odds ratio = (A*D) / (B*C) Odds ratio = (61*48) / (39*52) Odds ratio = 144;Odds ratio, and when by equating the two statistics we are sometimes forcing OR to be something it is not Another statistic, which is often also perceived as a relative risk, is the hazard ratio (HR) We encounter it, for example, when we fit the Cox model to survival data Under proportional hazards it is probably "natural" to thinkRelative risk, odds, odds ratio, and others The concept and method of calculation are explained for each of these in simple terms and with the help of examples The interpretation of each is presented in plain English rather than in technical language Clinically useful notes are provided, wherever necessary J Clin Psychiatry 15;76(7)e857




Biostatistics Primer What A Clinician Ought To Know Hazard Ratios Journal Of Thoracic Oncology




Odds Ratio And Hazard Ratio For Complications Download Table
Hazard Ratio Vs Relative Risk Vs Odds Ratio / Eposters How Big Is A Big Hazard Ratio Risk ratios (or relative risk) hazard ratio is frequently interpreted as risk ratio (or relative risk), but they are not technically the same In the example above, if the adjusted odds ratio were interpreted as a relative risk, it would suggest that the risk of antibiotic associated diarrhoea isClosure of mesenteric defects increased the risk for severe postoperative complications (54 4·3% for closure vs 35 2·8% for nonclosure, odds ratio 1·55, 95% CI 1·01–2·39, p=0·044), mainly because of kinking of the jejunojejunostomy Why does the analysis of reoperation due to small bowel obstruction use hazard ratio, and the In cohort A, imagingbased progressionfree survival was significantly longer in the olaparib group than in the control group (median, 74 months vs 36 months;Odds ratio, and when by equating the two statistics we are sometimes forcing OR to be something it is not Another statistic, which is often also perceived as a relative risk, is the hazard ratio (HR) We encounter it,




Hazard Ratio Vs Odds Ratio ただの悪魔の画像
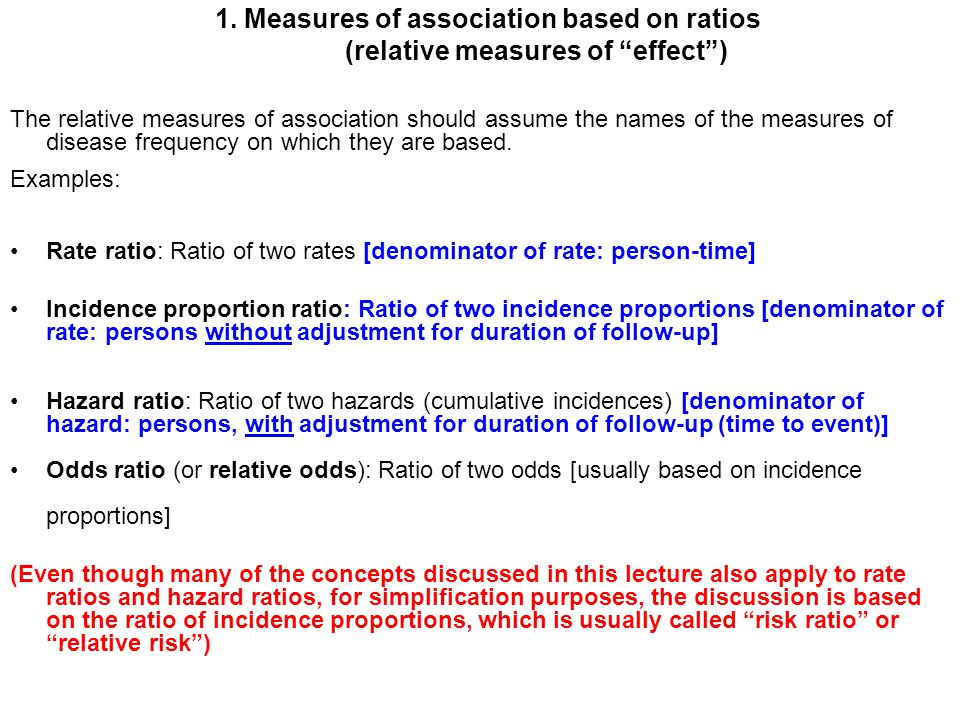



Measures Of Association Ppt Download
We would interpret this to mean that the odds that a player passes the test by using the new program are 144 times the odds that a player passes the test by using the old program In other words, the odds that a player passes the test are increased by using theHazard ratios differ from relative risks (RRs) and odds ratios (ORs) in that RRs and ORs are cumulative over an entire study, using a defined endpoint, while HRs represent instantaneous risk over the study time period, or some subset thereof ;RR and OR are commonly used measures of association in observational studies In this video I will discuss how to interpret them and how to apply them to pat




Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1




How To Calculate Odds Ratio And Relative Risk In Excel Statology
Examples of measures of association include risk ratio (relative risk), rate ratio, odds ratio, and proportionate mortality ratio Risk ratio Definition of risk ratio A risk ratio (RR), also called relative risk, compares the risk of a health event (disease, injury, risk factor, or death) among one group with the risk among another group It does so by dividing the risk (incidence For the majority of clinical trials, relative risk and odds ratio can be considered interchangeable as a measure of the relative change in the risk of a preventable event The hazard ratio is a related measure that weights the risk change according to when events occur over time Absolute risk reduction represents the absolute change in risk (expressed in percentage points)This is called the odds ratio;



Hazard Ratio Calculator Calculate Hazard Ratio Hr Confidence Intervals P Value




Understanding Systematic Reviews And Meta Analysis Archives Of Disease In Childhood
Ratio and odds ratio/risk ratio – Hazard/rate ratio ratio of incidence rates – Odds/risk ratio ratio of proportions By taking into account time, you are taking into account more information than just binary yes/no Gain power/precision Logistic regression aims to estimate the odds ratio;An odds ratio is the ratio of two odds In epidemiological parlance it is the odds of infection for those exposed to a risk factor, divided by the odds of infection for those not exposed to thatOdds ratio vs relative risk Odds ratios and relative risks are interpreted in much the same way and if and are much less than and then the odds ratio will be almost the same as the relative risk In some sense the relative risk is a more intuitive measure of effect size Note that the choice is only for prospective studies were the distinctionThe hazard




Frontiers Odds Ratio Or Prevalence Ratio An Overview Of Reported Statistical Methods And Appropriateness Of Interpretations In Cross Sectional Studies With Dichotomous Outcomes In Veterinary Medicine Veterinary Science




Delta Method Standard Errors
Hazard ratios differ from relative risks (RRs) and odds ratios (ORs) in that RRs and ORs are cumulative over an entire study, using a defined endpoint, while HRs represent instantaneous risk over the study time period, or some subset thereof Hazard ratios suffer somewhat less from selection bias with respect to the endpoints chosen and can indicate risks that happen before the», on utilise l'Odds Ratio (OR) Odd en français se traduit par la cote, terme bien connu des turfistes La cote de la préparation X est le rapport soit 1/5 (1 contre 5 pour les turfistes) Celle des autres préparations est de soit 1/10 L'Odds Ratio (OR) est le rapport des cotes OR 0,2/0,1 = 2 Cela s'interprète de la manière suivante Now let's take a HR less than 1 Let's say that in your experiment the calculated Hazard Ratio is equal to 065 This is how you can interpret and report it The mortality rate in a group of smokers drops by 35% compared to the group of highcalorie diet The mortality rate among smokers is 065 times of that among patients with a highcalorie diet




Interpreting Odds Ratio Senguptas Research Academy




Hazard Ratio Wikipedia
The second odds ratio is a summary across whatever stratumspecific odds ratios are available;
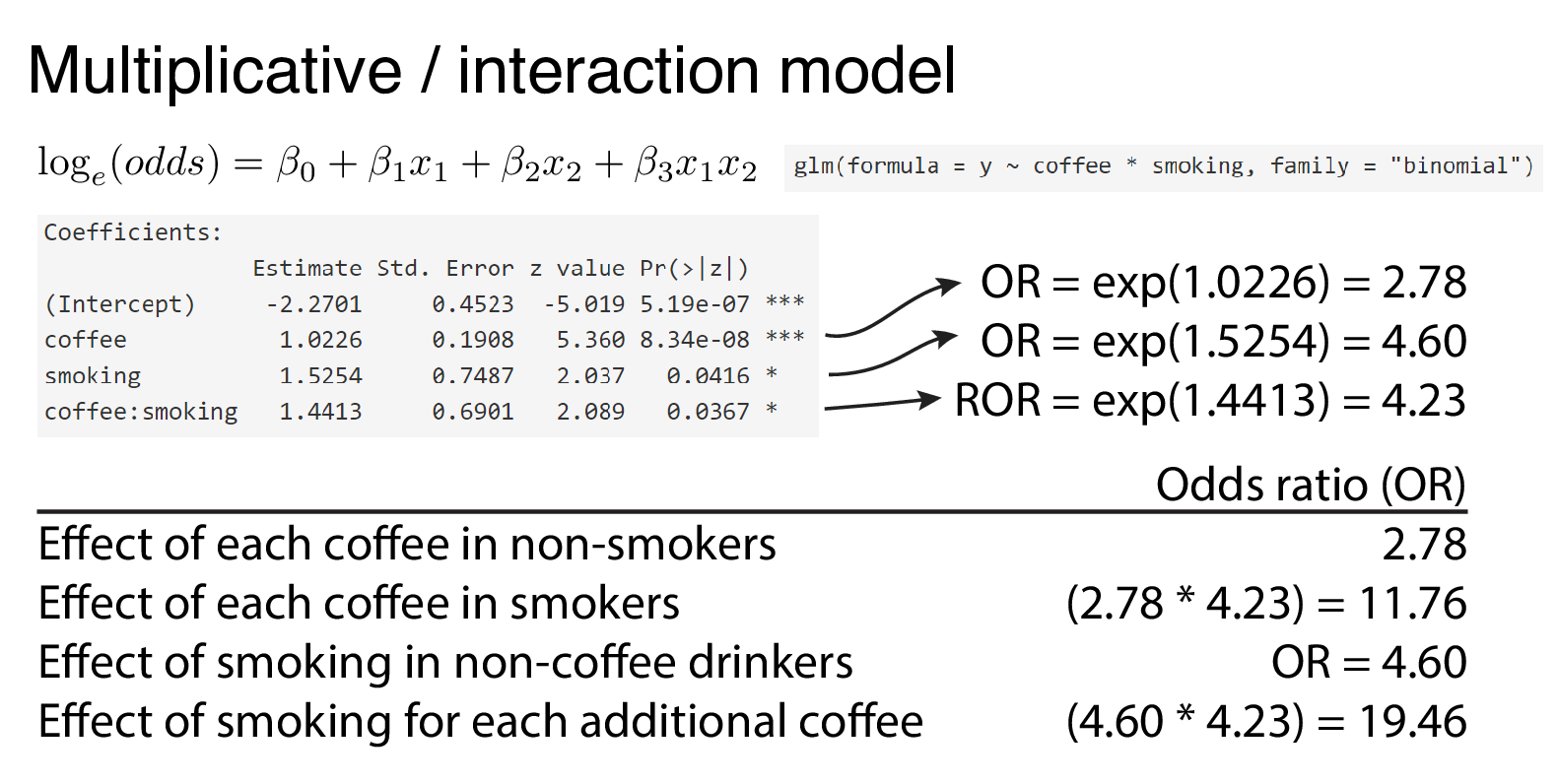



9 2 Binary Logistic Regression R For Health Data Science




Hazard Ratio Vs Odds Ratio ただの悪魔の画像




Hazard Ratios For Progression Free And Overall Survival And Odds Ratios Download Scientific Diagram




A Forest Plot Showing The Hazard Ratio And 95 Confidence Intervals Download Scientific Diagram



1
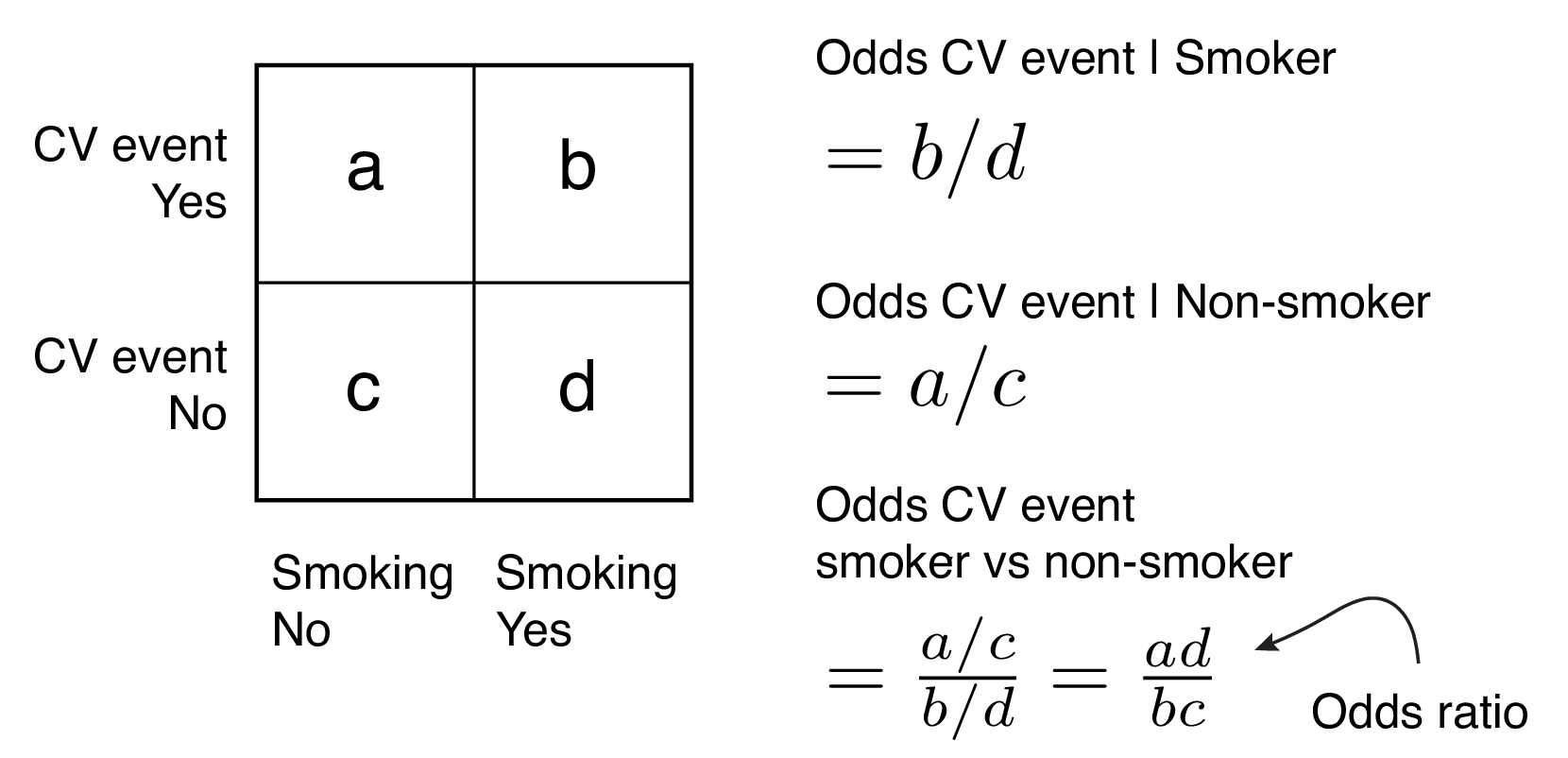



9 2 Binary Logistic Regression R For Health Data Science




Meta Analysis Odds Ratio




Simple Way To Visualise Odds Ratios In R Stack Overflow




Forest Plot An Overview Sciencedirect Topics




Pdf When To Use The Odds Ratio Or The Relative Risk Semantic Scholar



A Stratified Analysis




Relative Risks And Odds Ratios What S The Difference Mdedge Family Medicine




Relative Risk Odds Ratios Youtube




Tutorial About Hazard Ratios Students 4 Best Evidence




Outcomes Shown For A Odds Ratio Analysis And B Hazard Ratio Download Scientific Diagram




Network Meta Analysis Estimated Hazard Ratios Hrs For Comparison Of Download Scientific Diagram




A Beginner S Guide To Interpreting Odds Ratios Confidence Intervals And P Values Students 4 Best Evidence




Interpreting Hazard Ratios Youtube




Measures Of Association Ppt Download




Statistics For Afp Dr Mohammad A Fallaha Afp




Simple Way To Visualise Odds Ratios In R Stack Overflow



Ctspedia Ctspedia Oddsrisk




Statistics 103 Monday July 10 17 Survival Analysis




Pdf What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios Semantic Scholar



Interpretation Of Odds Ratio And Fisher S Exact Test By Sergen Cansiz Towards Data Science




Hazard Ratio Vs Odds Ratio ただの悪魔の画像



2



What Is The Difference Between The Risk Ratio Rr And The Odds Ratio Or Quora
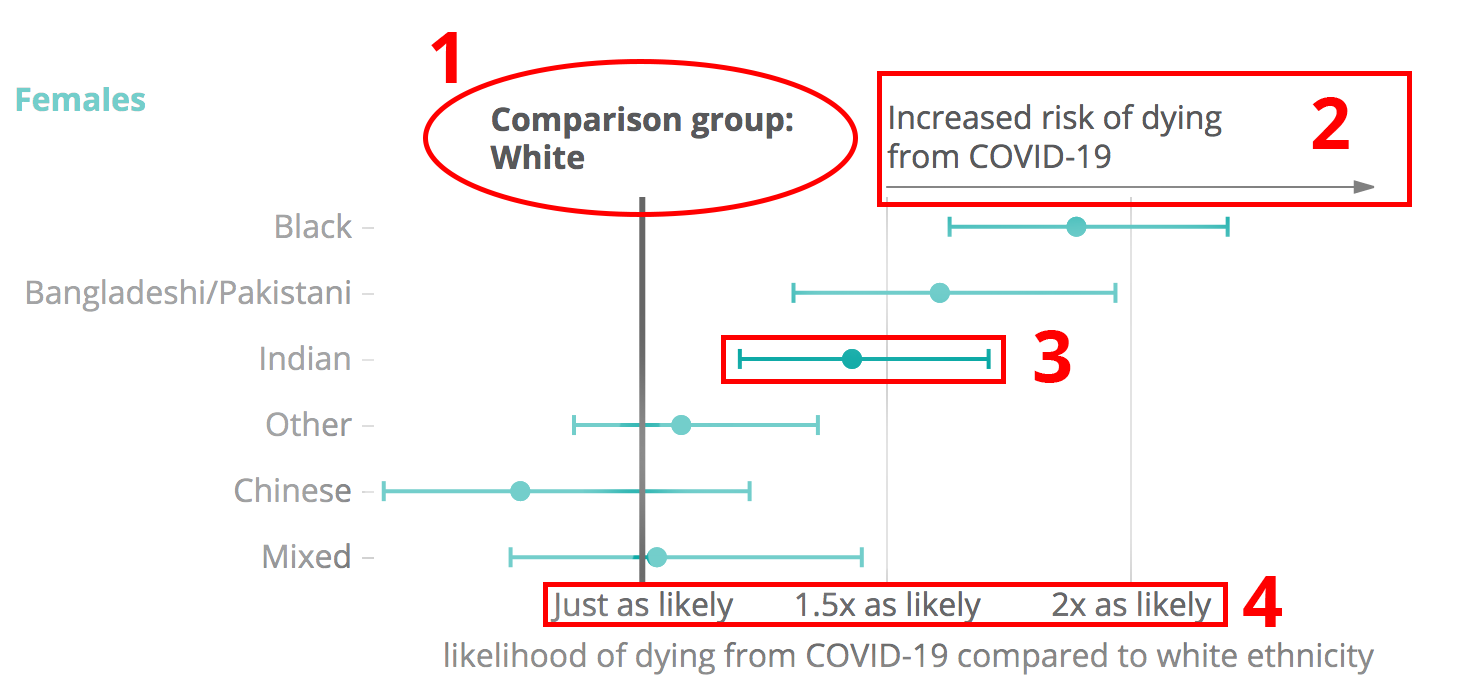



Against All Odds How To Visualise Odds Ratios To Non Expert Audiences Henry Lau




Crude And Adjusted Measures Of Odds Ratio Or And Hazard Ratio Hr Download Table




Converting An Odds Ratio To A Range Of Plausible Relative Risks For Better Communication Of Research Findings The Bmj




Relative Risk Wikipedia




How To Calculate An Odds Ratio Youtube




Odds Ratio Wikipedia



2



1



How To Interpret And Use A Relative Risk And An Odds Ratio Youtube




Odds Ratios Ors From The Multivariate Logistic Regression Analysis Download Scientific Diagram



How To Remember The Differences Between Odds Ratio Hazard Ratio And Likelihood Ratio And In What Instances They Should Be Applied Quora




Eposters How Big Is A Big Hazard Ratio




Pdf Odds Ratio Hazard Ratio And Relative Risk




What Does An Odds Ratio Or Relative Risk Mean



Plos One Influence Of Clinicopathological Characteristics And Comprehensive Treatment Models On The Prognosis Of Small Cell Carcinoma Of The Cervix A Systematic Review And Meta Analysis



2




Research Techniques Made Simple Interpreting Measures Of Association In Clinical Research Sciencedirect
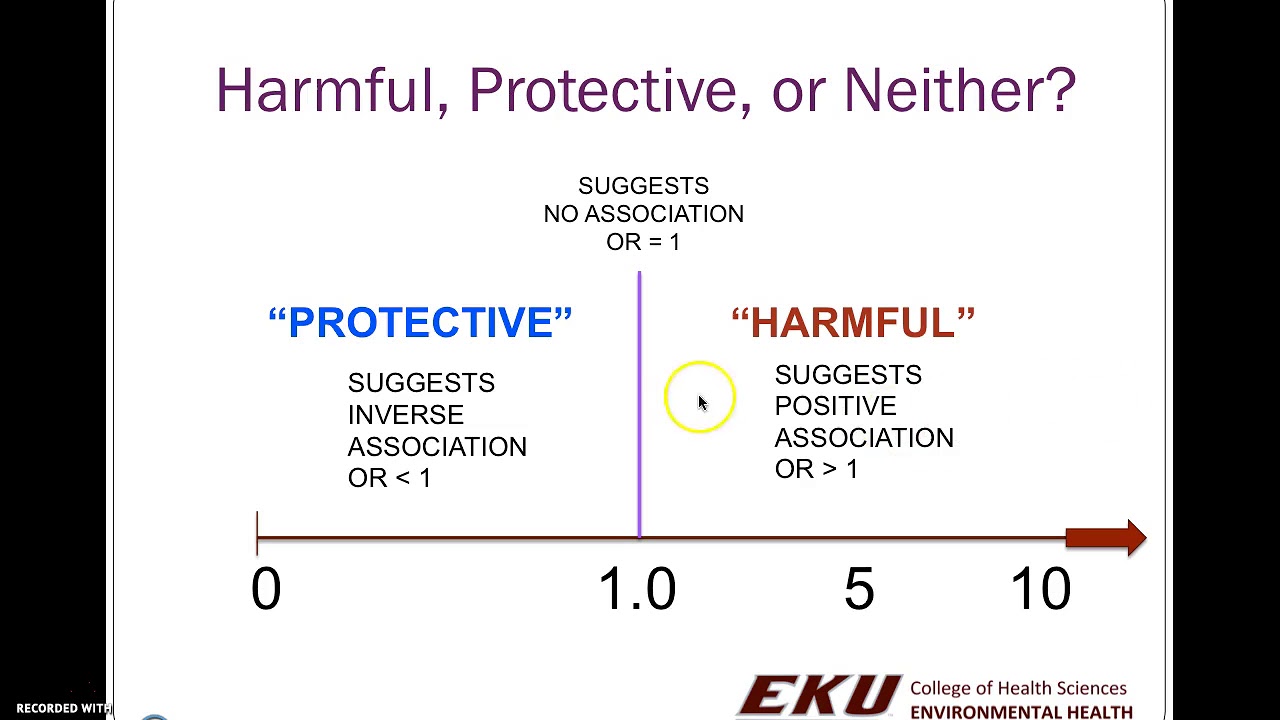



Part 1 Of 3 Interpreting Odds Risk And Rate Ratio Results With 95 Ci Youtube




Measures Of Effect Relative Risks Odds Ratios Risk Difference And Number Needed To Treat Sciencedirect



2




Hazard Ratio Vs Odds Ratio ただの悪魔の画像




Biostatistics Primer What A Clinician Ought To Know Hazard Ratios Journal Of Thoracic Oncology




Odds Ratios And Risk Ratios Youtube




Pdf What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios Semantic Scholar




Ppt Point Estimation Odds Ratios Hazard Ratios Risk Differences Precision Powerpoint Presentation Id




What Does An Odds Ratio Or Relative Risk Mean




Meta Analysis Odds Ratio



Hazard Ratio Vs Odds Ratio ただの悪魔の画像




What Does An Odds Ratio Or Relative Risk Mean




Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios




Statistics In Medicine Ppt Download




On Biostatistics And Clinical Trials Understanding The Endpoints In Oncology Overall Survival Progression Free Survival Hazard Ratio Censored Value
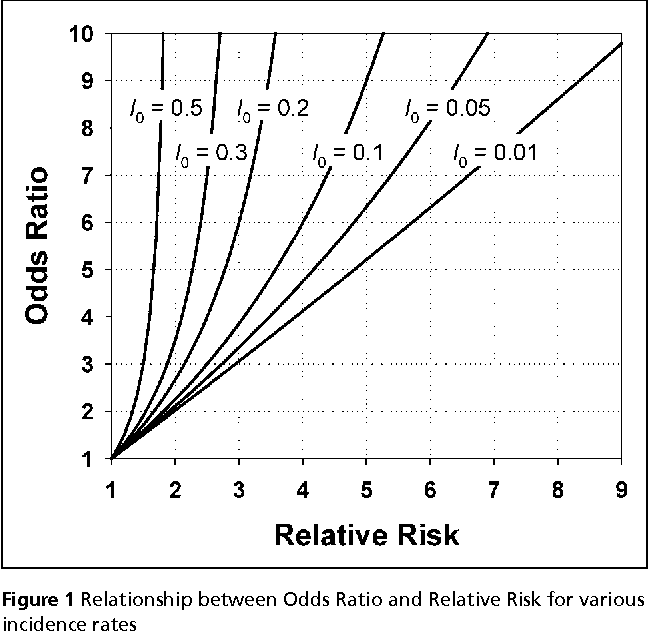



Pdf When To Use The Odds Ratio Or The Relative Risk Semantic Scholar




Tutorial About Hazard Ratios Students 4 Best Evidence




Tutorial About Hazard Ratios Students 4 Best Evidence




Odds Ratio Relative Risk Calculation Definition Probability Odds Youtube




In A Meta Analysis Of Adjusted Estimates From Observational Studies Can I Pool Or With Hr And Rr Probably Not How Can I Transform Hr To Or



Pdf What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios
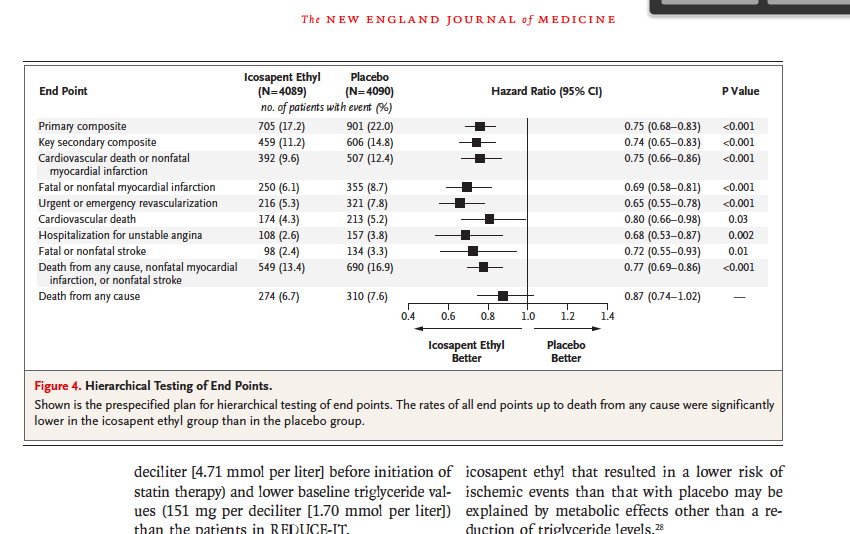



Hazard Ratio Vs Odds Ratio ただの悪魔の画像




Interpreting Hazard Ratios The Bmj




Hazard Ratio Relative Risk Or Odds Ratio Of Selected Outcomes For The Download Table




Odds Ratio Article




Relative Risk Wikipedia




Odds Ratios And Log Odds Ratios Clearly Explained Youtube



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿